

News
19.08.2025
Blowers play a vital role in countless industrial and commercial applications, from dust collection systems and combustion air supply to HVAC and pneumatic conveying. But if you’ve ever wondered “how does a blower work?”, this article explains the principles behind their operation, the main types of blowers, and how they support efficient air movement in demanding environments.
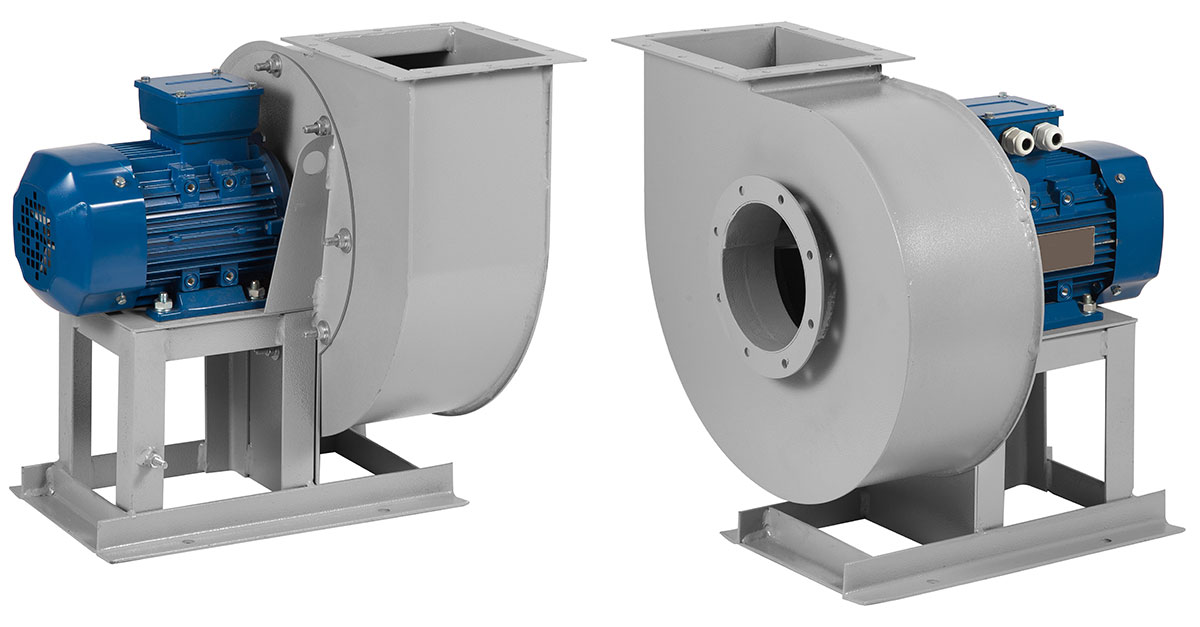
A blower is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of air or gas and forces it to move through a system. Unlike fans, which are designed primarily for low-pressure air movement, blowers operate at higher pressures, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial processes.
So, how does a blower work? The principle is relatively straightforward:
This cycle creates a continuous and controlled airflow, making blowers reliable for applications that require stable pressure and volume.
Different blowers work in slightly different ways depending on their design. The two most common categories are:
Understanding how a blower works highlights why they are critical in so many industries. Common applications include:
So, how does a blower work? In essence, a blower converts mechanical energy into air movement and pressure, enabling countless industrial systems to operate safely and efficiently. Whether centrifugal or positive displacement, the right blower ensures reliable performance and long-term system protection.
Return To NewsKeep up to date with our
Our Range

Worldwide shipping
International standards
High performance

