


News
20.10.2025
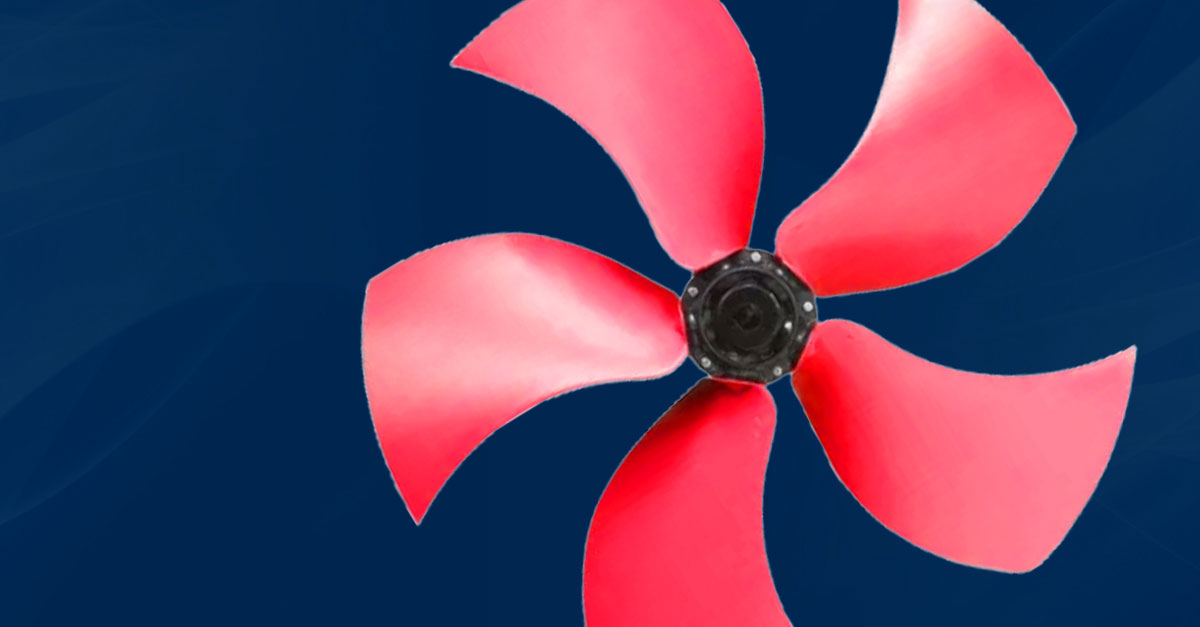
In axial fans, fan wings refer to the blades or impellers responsible for creating airflow. Just like an aircraft wing generates lift, fan blades move air by creating pressure differences as they rotate. Mounted to a central hub, these wings draw air in and push it out along the fan’s axis — hence the term axial fans.
The cross-section of a fan wing is shaped like an airfoil, helping generate smooth, efficient airflow. This reduces turbulence and energy loss while keeping noise levels low. A well-designed wing ensures stable airflow and optimal performance across different operating speeds.
The pitch (angle of the wing) determines how much air the fan can move. Steeper angles produce more airflow and pressure but can increase noise and power usage.
The number of wings also influences performance — fewer blades often suit high-flow, low-pressure systems, while more blades are better for higher-pressure applications or when quieter operation is needed.
Fan wings can be made from aluminium, steel, composite materials, or engineered plastics, depending on the application. The chosen material impacts weight, corrosion resistance, and strength, especially in high-temperature or corrosive environments.
To achieve high efficiency, fan wings must minimise energy losses caused by turbulence or poor air distribution. Blade shape, tip design, and surface smoothness all influence how efficiently air passes through the fan.
Noise is a major factor in fan design. Advanced fan wings feature optimised trailing edges, reduced tip clearance, and smooth airfoil surfaces to lower sound levels without compromising performance.
Fan designers balance airflow volume and pressure generation. Large-diameter fans with shallow pitches are ideal for ventilation, while smaller, steeper-pitched wings perform better in high-resistance systems such as ducted installations.
Applications exposed to high heat, moisture, or corrosive gases require specially treated materials or coatings. The wing design and hub connection must withstand harsh environments without performance degradation.
Fan wings are at the core of an axial fan’s performance. Their design - from blade angle and material to aerodynamic profile - directly affects airflow efficiency, noise, and energy consumption. Understanding these factors ensures that each fan operates at its highest potential, tailored perfectly to the needs of its environment.
Return To NewsKeep up to date with our
Our Range

Worldwide shipping
International standards
High performance

